Traffic accidents continue to be a leading public health problem. Although significant strides have been made in improving road safety, motor vehicle crashes remain the leading cause of death of people. Asian countries having only 16% of vehicle population in world accounts for 44% of the global road accident fatalities. Highly motorised countries having 60% of vehicle population has a fatality rate of only 14%.
Tamil Nadu is losing Rs.700 crores a year in road accidents. The State stands second in the Accident Risk Index in the country, and the number of accidents is estimated to increase fourfold by 2025. The trend of road accidents in
Table 1.1 Accidents in Our Country
|
State |
Persons Killed |
Person Injured | |||
|
1999 |
2004 |
1999 |
2004 | ||
|
Andra Pradesh |
9212 |
10552 |
33966 |
50895 | |
|
Tamil Nadu |
9653 |
9507 |
41444 |
57283 | |
|
Maharastra |
9807 |
9875 |
51429 |
47394 | |
|
Uttar Pradesh |
9984 |
9946 |
14330 |
13188 | |
|
Total |
81966 |
92543 |
375051 |
464583 | |
Table1.2: Number of Accidents and Persons involved in Tamil Nadu during the year 2002 to 2005
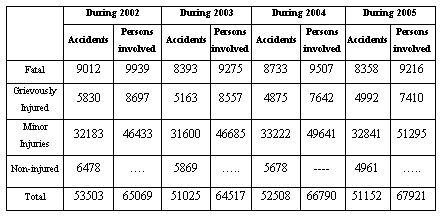
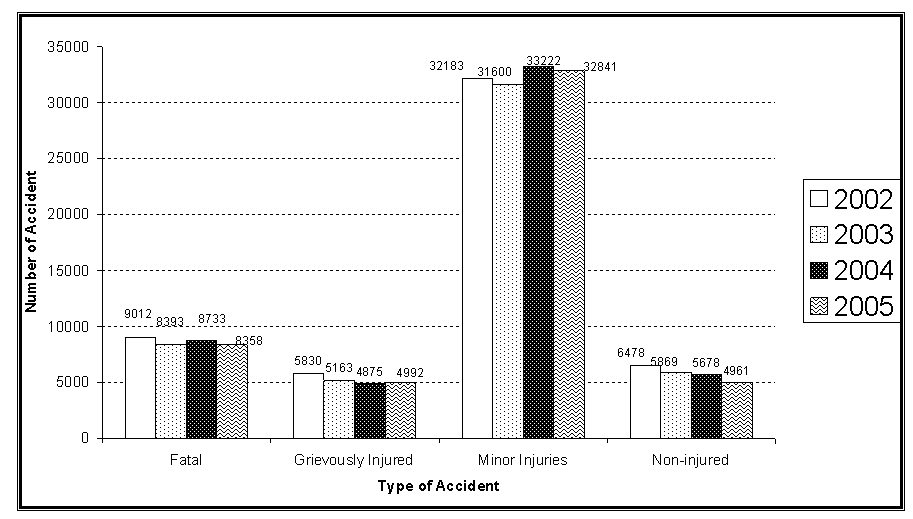
Fig1.1: Number of Persons involved in accident (Tamil Nadu During the year 2002 t0 2005)
Accident analysis and infrastructure investment decisions require accurate, reflective data from which to draw conclusions. Accident data recording, maintenance and analysis software is required by various agencies like Highway Department, Police, Insurance Agency, University and Consultants. In developed countries exclusive software is available for recording and analysis of accident data permitting access to the agencies concerned. This way accident data base is maintained for the whole country but in
The data collection by the police is insufficient to draw engineering remedial measures. Effective recording and analysis will help in identifying vulnerable locations and for planning emergency response system. In this study an attempt has been made to develop a web based GIS accident analysis system to record and analyse the accident details and this system is planned for the usage of all user agencies through wide area network.
1.2 NEED FOR STUDY
Most of the accidents results from human error, and carelessness on the part of the drivers or pedestrians. However, the probability of occurrence, and its severity, can often be reduced by the application of proper traffic control devices, and good roadway design features. The success or failure of such control devices and design specifications however, depends extensively upon the analysis of traffic accident records at specific locations. It has long been recognized that the most effective means towards accident reduction lies in a systematic and scientific approach based on the use of accurate and reliable traffic accident data.
The report for the GRSP identifies weakness in the quality of existing data, accident databases in many developing countries should be improved through greater use of accident reporting and recording systems.
In developed countries accident record keeping has be given much priority by concerned government agencies. Maryland State Highway Administration, Crash data is recorded by the state, country, local or federal law enforcement officer at the scene of the reportable accident. Later, the data may be reviewed and edited. Typically, within 10 days of the accident occurrence, the report is submitted to the
Much of the accident information available in police files is all too often incomplete and therefore has not been utilized to the fullest extent. There is a need for better information of the circumstance of collisions, especially with regards to location in order to come up with a general picture of the data. Fig 2.1 shows various agencies which require accident data. More precise location data could help to evolve programs for enforcement, education, maintenance, vehicle inspection, planning emergency medical services, and engineering measures to improve highways defects.
At present, the system of traffic accident investigation and reporting suffers due to organisational and technical problems. Currently, there is an information gap with regard to traffic accident data due to the following reasons.
- The current traffic accidents database system is ineffective due to non-submission in IRC stipulated forms.
- Location information about accident is not complete.
- In the traffic accident investigation and reporting is carried due to non technical people.
- New tools and technologies are not used.
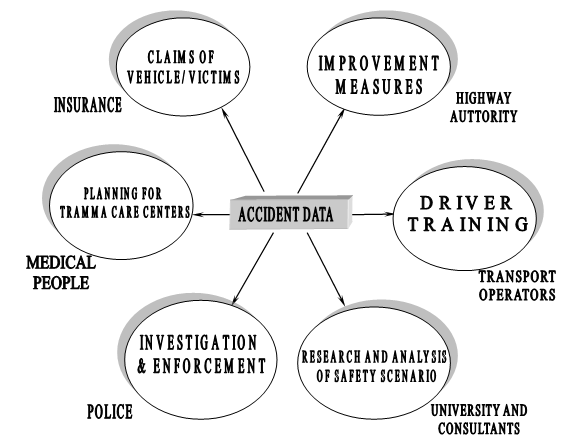
Fig 1.2.Various Agencies Using Accident Data
So far, there is no integrated database that accounts for accidents statistics for the whole country in
1.2 OBJECTIVES
- To build accident database and structured reporting system, to store, manipulate accident data.
- To develop a user interface in GIS platform using .Net (Dot Net) programming language.
- To develop accident analysis facilities as required by user agencies.
1.2 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
The study has the following limitations:
The available accident data has been used in the study.
The causes for accidents are not explicit.
Network analysis has been carried using distance as the criteria.
1.3 ORGANISATION OF THE PROJECT REPORT
Chapter 1 gives the introduction and the background of the project work. Chapter-2 presents the Literature Review, which is very essential to understand and also to discover newer techniques, Chapter 3 deals with the Study Area, Data collection and the methodology. Chapter 4 present the introduction about the GIS and Programming software used to develop the web based GIS Accident Analysis System and explains development of accident analysis system. Chapter 5 explains Application of Accident Analysis System. Chapter 6 discusses the recommendations and conclusion.